
Pharmaceutical Financial Health Check: Key Steps | Capsna
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most profitable yet complex sectors, requiring continuous financial assessment to maintain stability and growth. A financial health check ensures that pharmaceutical companies stay competitive, comply with regulations, and optimize profitability. Whether you’re a financial analyst, CFO, or business owner, understanding the financial well-being of a pharmaceutical firm is crucial for long-term success.
In this guide, we will explore the essential steps, key performance indicators (KPIs), and best practices for conducting a comprehensive financial health check in the pharmaceutical industry.
Understanding Financial Health in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical companies face unique financial challenges, including high R&D costs, regulatory compliance, and fluctuating market demands. Assessing financial health requires analyzing several aspects, such as revenue trends, profitability, cash flow, and cost efficiency.
Why is a Financial Health Check Essential?
- Ensures financial stability and sustainability
- Identifies risks and opportunities for growth
- Enhances investor confidence and market value
- Helps in regulatory compliance and risk management
- Improves cost control and resource allocation
A financial health check is not just about looking at numbers—it’s about understanding the overall financial ecosystem of a pharmaceutical business.
Key Components of a Financial Health Check
1. Revenue and Profitability Analysis
Revenue is the lifeblood of any business. In the pharmaceutical sector, revenue streams come from drug sales, licensing agreements, and research collaborations.
Key metrics to analyze:
- Revenue growth rate: Measures how sales are increasing or decreasing over time.
- Gross profit margin: Indicates profitability after subtracting the cost of goods sold.
- Net profit margin: Evaluates overall profitability after all expenses, taxes, and interest.
A steady increase in revenue and a healthy profit margin indicate strong financial health.
2. Cost Structure and Expense Management
Pharmaceutical firms incur significant costs, especially in research and development (R&D), production, marketing, and compliance.
Areas to examine:
- R&D expenditure as a percentage of revenue
- Operational costs and manufacturing efficiency
- Marketing and distribution expenses
Optimizing expenses without compromising quality is crucial for financial sustainability.
3. Cash Flow Management
Cash flow determines a company’s ability to meet its obligations, such as supplier payments, employee salaries, and research investments.
Key cash flow indicators:
- Operating cash flow: Cash generated from core business activities.
- Free cash flow: Cash remaining after capital expenditures.
- Cash conversion cycle: Measures the time taken to convert inventory into cash.
A positive cash flow ensures business continuity and financial resilience.
4. Liquidity and Solvency Analysis
Liquidity measures a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations, while solvency assesses long-term financial stability.
Key liquidity ratios:
- Current ratio: Current assets divided by current liabilities. A ratio above 1 indicates good liquidity.
- Quick ratio: More stringent than the current ratio, excluding inventory from current assets.
Key solvency ratios:
- Debt-to-equity ratio: Assesses financial leverage and risk.
- Interest coverage ratio: Measures the ability to cover interest expenses.
Balancing liquidity and solvency is essential to avoid financial distress.
5. Compliance and Risk Management
The pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated, requiring adherence to strict financial and operational guidelines.
Critical risk factors to assess:
- Regulatory compliance costs
- Patent expirations and generic competition
- Supply chain disruptions
- Foreign exchange risks in global markets
A well-structured risk management strategy safeguards the company’s financial health.
6. Return on Investment (ROI) and Growth Potential
Investors and stakeholders evaluate ROI to determine profitability and growth potential.
Important ROI metrics:
- Return on assets (ROA): Measures how efficiently assets generate profit.
- Return on equity (ROE): Evaluates profitability relative to shareholder equity.
- Earnings per share (EPS): Indicates profitability on a per-share basis.
A high ROI reflects effective financial and operational management.
Steps to Conduct a Financial Health Check in a Pharmaceutical Company
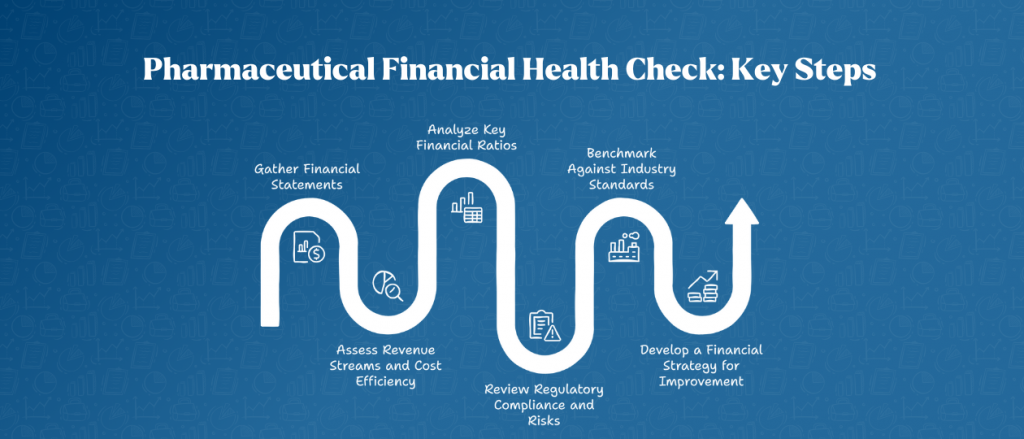
Step 1: Gather Financial Statements
Analyze the latest balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to get an overview of the company’s financial position.
Step 2: Assess Revenue Streams and Cost Efficiency
Identify the primary revenue sources and major cost drivers to evaluate profitability and efficiency.
Step 3: Analyze Key Financial Ratios
Calculate and interpret liquidity, solvency, and profitability ratios to assess financial stability.
Step 4: Review Regulatory Compliance and Risks
Ensure adherence to financial and operational regulations to avoid legal and financial penalties.
Step 5: Benchmark Against Industry Standards
Compare financial performance with industry peers to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Step 6: Develop a Financial Strategy for Improvement
Based on the analysis, implement strategies to enhance revenue, reduce costs, and improve financial health.
Best Practices for Maintaining Financial Health
- Optimize R&D Spending: Focus on high-potential drugs and strategic partnerships.
- Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency: Reduce costs and mitigate risks by diversifying suppliers.
- Monitor Market Trends: Stay updated on regulatory changes and industry shifts.
- Strengthen Cash Flow Management: Maintain adequate cash reserves and improve collections.
- Invest in Digital Transformation: Utilize financial analytics for better decision-making.
Conclusion
Conducting a financial health check in the pharmaceutical industry is essential for ensuring stability, profitability, and compliance. By analyzing revenue, costs, cash flow, liquidity, and risks, companies can make informed financial decisions and drive sustainable growth. Regular financial assessments not only help in risk mitigation but also enhance investor confidence and market positioning.
By following best practices and leveraging financial analytics, pharmaceutical firms can maintain a strong financial foundation and continue delivering innovative healthcare solutions to the world.
FAQs:
How often should a pharmaceutical company conduct a financial health check?
What are the biggest financial risks in the pharmaceutical.